Here are some key aspects of syntax in English:
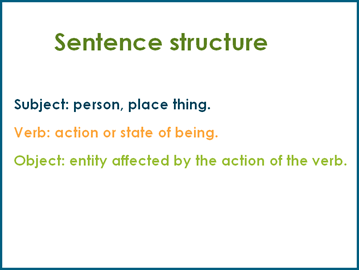
Sentence structure
Sentence Elements: The basic elements of a sentence are the subject, verb, and object.
Subject: The person, place, thing, or idea that is performing the action or being described.
Verb: The action or state of being.
Object: The entity that is affected by the action of the verb.
Word order
Standard Word Order: The typical English sentence follows a Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) order.
Example: She (subject) reads (verb) books (object).

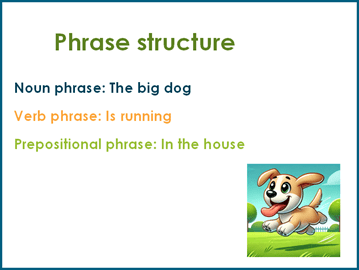
Phrase structure
Noun Phrase (NP): A phrase that functions as a noun within a sentence.
Example: The big dog (determiner + adjective + noun).
Verb Phrase (VP): A phrase that functions as a verb within a sentence.
Example: Is running (auxiliary verb + main verb).
Prepositional Phrase (PP): A modifying phrase consisting of a preposition and its object.
Example: In the house (preposition + noun phrase).
Clauses
Independent Clause: A group of words that can stand alone as a sentence.
Example: She likes coffee.
Dependent Clause: A group of words that cannot stand alone and must be connected to an independent clause.
Example: Although she likes coffee, she drinks tea.

Agreements
Subject-Verb Agreement: The subject and verb must agree in number (singular or plural).
Example: The cat runs. The cats run.
Pronoun-Antecedent Agreement: Pronouns must agree with their antecedents in number, gender, and person.
Example: Every student must bring their own lunch.

Modifiers
Adjectives and Adverbs: Adjectives modify nouns, and adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Example: The quick (adjective) fox jumps. The fox jumps quickly (adverb).

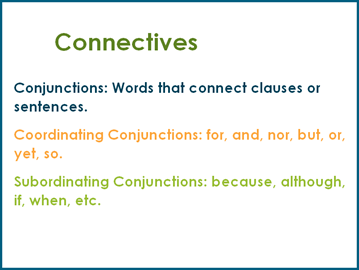
Connectives
Conjunctions: Words that connect clauses or sentences.
Coordinating Conjunctions: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
Subordinating Conjunctions: because, although, if, when, etc.
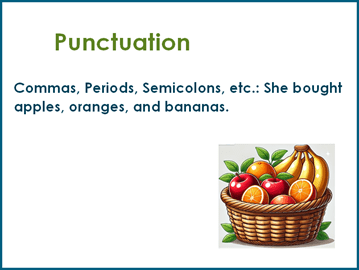
Punctuation
Commas, Periods, Semicolons, etc.: Punctuation marks are used to clarify meaning by indicating separation of words into sentences, clauses, and phrases.
Example: She bought apples, oranges, and bananas.
Importance of syntax
Syntax is crucial for:
Clarity: Proper syntax ensures that sentences are clear and understandable.
Meaning: Different syntactical arrangements can change the meaning of a sentence.
Example: The dog bit the man. vs. The man bit the dog.
Flow: Good syntax helps in creating a smooth and natural flow in writing and speech.
In essence, syntax is about the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language, and it plays a key role in effective communication.

