What does an engine do?
An engine is a machine that converts energy into motion. It provides power to vehicles like cars, airplanes, boats, and even rockets, allowing them to move.
How does an engine work?
Most engines follow these steps:
Fuel in: The engine takes in fuel (like gasoline) and air.
Explosion: The fuel burns inside the engine, creating a small explosion.
Power: The explosion pushes parts inside the engine, making them move.
Wheels turn: This movement helps turn the wheels, propellers, or other parts that make a machine go.
Types of engines
Gasoline engines: Found in most cars. They burn fuel to make small explosions that power the car.
Electric motors: Found in electric cars and trains. They use electricity instead of fuel.
Jet engines: Found in airplanes. They take in air, mix it with fuel, and push out hot air to make the plane fly.
Steam engines: Old trains and boats used these. They heat water to make steam, which pushes big wheels.
How does a gasoline engine work? (internal combustion engine)
Most cars use a four-stroke internal combustion engine, which burns fuel inside a chamber. Here’s how it works in four steps:
Intake: The engine takes in a mix of air and fuel.
Compression: The piston squeezes the mixture, making it highly flammable.
Power (Combustion): A spark plug ignites the fuel, causing a mini-explosion that pushes the piston down.
Exhaust: The waste gases from the explosion exit through the exhaust pipe.
This cycle repeats over and over, creating energy that turns the wheels of the car.

Fun fact: A typical car engine runs thousands of these tiny explosions every minute.
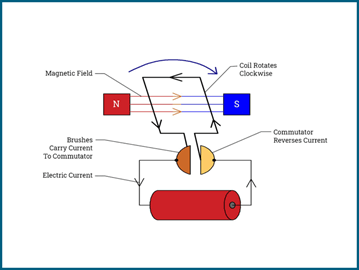
How do electric motors work?
Unlike gasoline engines, electric motors use electricity stored in batteries to create movement. Here’s how:
Battery Power: The battery sends electricity to a motor.
Magnetic Fields: The motor uses electromagnets to create rotation.
Wheels Turn: This rotation is transferred to the wheels, making the car move.
Electric motors are quieter, cleaner, and more efficient than gas engines. That’s why many new cars use electric motors.
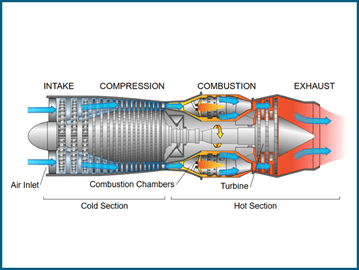
How do jet engines work?
Airplanes use jet engines, which suck in air, compress it, mix it with fuel, and ignite it. The hot gases rush out the back, pushing the plane forward.
Think of it like this: If you blow up a balloon and let go, the air rushing out propels the balloon forward—that’s the same way a jet engine works.
Steam engines
Before gasoline engines, trains and boats used steam engines. These worked by:
Heating water in a boiler to create steam.
The steam expands and pushes pistons or turbines.
The pistons turn wheels or propellers, moving the machine.

Fun fact: The first trains ran on steam engines, and some still exist today for special rides.
Rocket engines
Rocket engines are different from car or jet engines because they work in space, where there’s no air. They burn special fuel and push out hot gases at extreme speeds, launching the rocket forward.
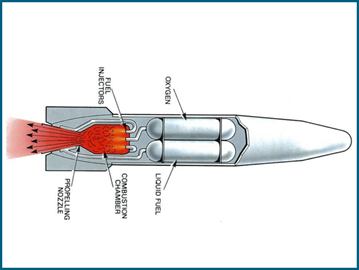
Cool fact: A rocket engine must push hard enough to break Earth’s gravity — over 17,000 miles per hour.

