Did you know there are several ways in which you can solve 2-digit addition? Here are four of the most common ways students learn to solve 2-digit (and for that matter 3-digit) addition problems.
We’ll use 89 + 34 as our 2-digit addition example.
Break Apart
Here the student breaks apart the addition problems using place value.
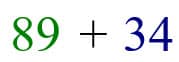
89 breaks into 8 tens and 9 ones, 34 into 3 tens and 4 ones.
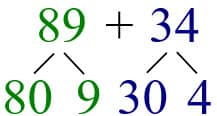
Then adding up the ones and the tens, it’s easier to solve the 2-digit addition.

Number Line
Using a number line, students can easily visualize the sum by using place values.
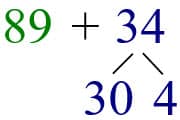
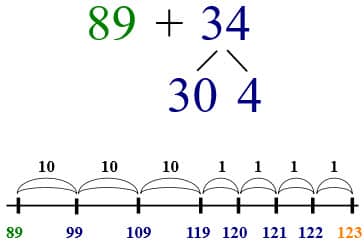
Starting at the bigger number 89, we start with moving forward by 3 tens and then 4 ones.
Vertical Addition
When you add vertically, you place the one number above the other, aligning the ones and the tens in columns.
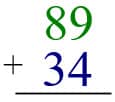
By adding the numbers vertically, you add the ones first. 4 + 9 = 13, or 1 ten and 3 ones. Be careful to place the numbers in the correct columns.
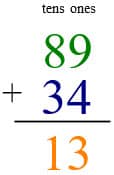
Then add the tens. 8 + 3 = 11 tens, or 110 ones.
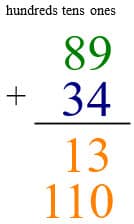
Now you have two new numbers to add 13 + 110 = 123. Add the ones first: 0 + 3 = 3, then the tens: 1 + 1 = 2, and, finally the hundreds: 0 + 1 = 1.
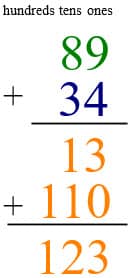
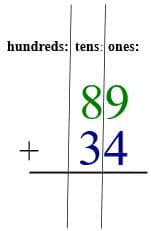
Algorithm
Placing the numbers vertically, using standard algorithm, you add the ones first, the tens second, in columns.
When you add the ones, you get 13 ones, or 1 ten and 3 ones. You carry the 1 ten into the tens column.
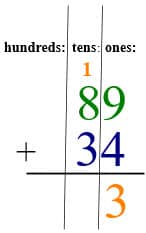
Then you add the tens. 1 + 8 + 3 = 12 tens, or 1 hundred and 2 tens. The 1 hundred carries across to the hundred column.
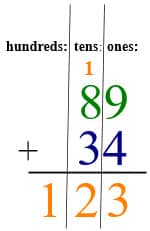
There you have it. Four ways to solve 2-digit addition problems.

